This article will give you a basic overview of how the internet functions and explain why you may not always see the advertised network speeds on your Server.
Your data does not travel the way you think it does
When you connecting to your server you may think that your computer is going directly from your home PC to your Server in a straight line such as going from A >>> B.
However this is not how the internet works. It looks more like this:
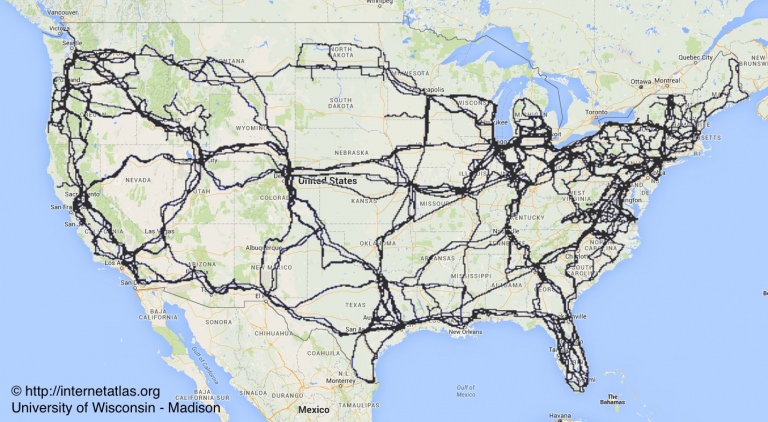
Your home PC is instead connecting to your ISP, who then passes the traffic to a 3rd-party called a peering partner, who then passes the traffic along until it reaches its destination. Each stop that your data makes is whats called a “Hop“.
The less Hops your data takes the more likely it is that you will have both higher transfer speeds as well as lower latency.
Why does the Internet work like this?
It functions like this for 2 primary reasons, reliability and cost.
By having a large and fast backbone the Internet can continue to function even if a major route goes offline as there are redundant paths to the same destination.
Secondly there is a large cost savings by having peers share traffic between networks at no or little cost. Without peers it would cost a tremendous amount of money just to send an email.
How to optimize my connections for the best possible speed on my server?
When trying to get the best speed possible you need to consider the following factors:
1). Location of the server (Source)
3). Server’s rated connection speed
4). Distance to client (Destination).
5). Client’s rated connection speed
6). Number of connections
7). Server load
Generally speaking this means that when choosing a Server you will want to choose a location that is closest to the destination where it will be used the most.
You will also want to consider the number of connections as well as this can impact your overall throughput. For example if you are transferring a file using SFTP with only allowing 1 connection at a time the transfer could be limited to something like 3MB/sec. Where as if you were to allow 5 total connections you could see each file transferring at a rate of 2MB/sec for an effective transfer rate of 10MB/sec.
One additional factor you will want to be aware of when seeing poor Internet speed is Server Load/Usage.
On Linux servers you can run the top command to check your current usage and load average. On Windows servers you can run Task Manager to check similar information.
Basically a server under a heavy or sustained load will not always be able to respond to network requests as quickly as it could when not under stress. The tests above were performed on a server with no additional programs running or outside network traffic. In your case your server will likely be under some load from programs running in the background resulting in slower results. Factors outside of your control such as DDOS attacks can also cause this as well.
An additional factor to consider is the Internet Speed of the location you are connecting to.
It is still common to see some home and business connections greatly limited in upload bandwidth. Even the fastest home Cable connections generally have a maximum upload limit of 40/Mbit a sec which equals 5 Megabytes per second in data transfer. Unless you are on a home fiber connection and live close to the Data Center your server is located in your connection will likely not be able to hit maximum transfer speeds.
What does this mean if I have a IONOS Server?
If you have a IONOS Server hosted at the USA location this means that your server is located in Kansas. As you saw in the map above this is a great central location for users across the USA. Being that it is roughly equal distance to each coast a user in California should not notice a significant difference from a user in New York.
But please be aware that while IONOS aims to have great performance across the USA if your users are only going to be connecting from a specific region such as the East Coast then you may see better performance from a Server provider which hosts servers in Virginia instead of Kansas.
Internet Speed tests
Each Cloud/VPS with IONOS is rated for a connection between 300-400mbps. In the best case scenario you should see speeds such as the one below:

In this example my server is connecting to the closest possible test server using multiple connections.
Lets see how the connection is effected when limiting the test to only a single connection:

As you can see the upload speed is greatly limited over a single connection. This effect will become worse over longer distances.
Lets take things further and test additional locations using both multiple, and single connections:
Dallas, TX – Multi:

Dallas, TX – Single:

Chicago, IL – Multi:

Chicago, IL – Single:

Miami, FL – Multi:

Miami, FL – Single:

San Diego, CA – Multi:

San Diego, CA – Single:

As you can see across the USA performance is still quiet good no matter the location as long as multiple connections are used simultaneously. As you can see across the USA performance is still quite good no matter the location as long as multiple connections are used simultaneously.
This is why testing your speed using a single file download is inaccurate. Since only a single connection is used it will not use all of your available bandwidth.
What about from outside the USA?
For more fun lets try a few locations outside of the USA:
Berlin, Germany – Multi:

Berlin, Germany – Single:

For the Berlin results you may be confused. The reason the performance of a connection all the way to Berlin is roughly equal to a connection to Miami, FL is due to the IONOS Backbone. Since IONOS has very strong direct links between North America and Europe you can expect better results between these 2 regions.
But to get the best results in Europe you would want to setup a IONOS Server in the Germany or Spain Datacenter locations instead.
Let’s try some more sources that don’t take advantage of this backbone:
Coquimbo, Chile – Multi:

Coquimbo, Chile – Single:

Tokyo, Japan – Multi:

Tokyo, Japan – Single:

Cape Town, South Africa – Multi:

Cape Town, South Africa – Single:

As you can see while it is possible to access the server across the entire world you will not have the best experience unless you are are near the server’s location. This is why CDNs are often used as they help to limit the amount of data that needs to be pulled directly from the server instead of a much closer caching server.
Conclusion
I hope that this article helps you to better understand the large number of variables that go into determining how fast your server’s connection speed is.